

Hotline: 0906 201 222
I. There is / there are
There is/are luôn đứng trước một danh từ/cụm danh từ là chủ thể của câu.
|
There is + singular nouns (danh từ số ít) |
| There are + plural nouns (danh từ số nhiều) |
e.g.: There is one important reason why we must tackle the problem of global warming.
(Chúng ta phải giải quyết hiện tượng nóng lên toàn cầu vì một lí do rất quan trọng)
There are several reasons why we must tackle the problem of global warming.
(Chúng ta phải giải quyết hiện tượng nóng lên toàn cầu vì một số lí do)
II. Either A or B / neither A nor B
Cấu trúc ‘either A or B’ (hoặc A hoặc B), ‘neither A nor B’ (không A cũng không B) có thể đóng 3 kiểu vai trò trong câu:
· chủ ngữ
e.g. : Either Italy or France made it to the final round.
· tân ngữ
e.g. : I can drink neither beer nor wine.
· mệnh đề
e.g. : Either I find a well-paying job, or my parents will send me abroad.
Tuy nhiên, trong nội dung kiến thức S-V agreement, chúng ta sẽ học cấu trúc này với vai trò là chủ ngữ. Công thức như sau:
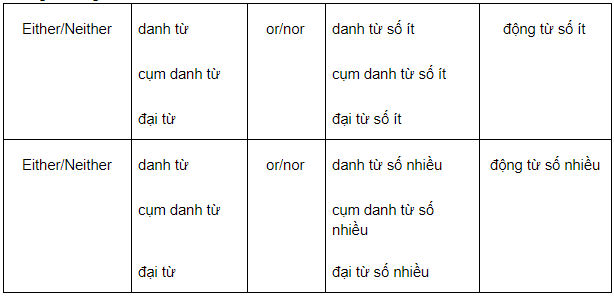
Ở vai trò này, động từ được chia dựa vào danh từ đứng cạnh nó.
e.g. : Neither Apple nor Samsung wants to settle the disagreement peacefully.
Either you or them take out the trash!
III. Both A and B
Cấu trúc ‘both A and B’ có thể là chủ ngữ, cũng có thể là tân ngữ trong câu. Tuy nhiên, trong nội dung kiến thức S-V agreement, chúng ta sẽ học cấu trúc này với vai trò là chủ ngữ. Khi đó, động từ LUÔN chia số nhiều.
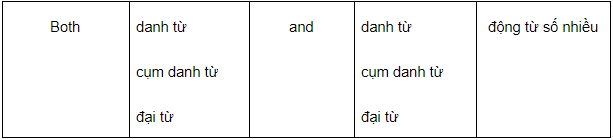
e.g. :
Both Japanese and Korean are difficult for me to study.
Both the local authority and the local people have made continuous attempts to stop street littering.
IV. A as well as B
Cấu trúc ‘A as well as B’ có thể là chủ ngữ, cũng có thể là tân ngữ trong câu. Tuy nhiên, trong nội dung kiến thức S-V agreement, chúng ta sẽ học cấu trúc này với vai trò là chủ ngữ. Khi đó, động từ LUÔN chia số ít.

e.g. :
The local authority as well as the local people has made continuous attempts to stop street littering.
My family can’t adopt a cat because my dad, as well as my sister, is allergic to cats’ fur.
V. Đại từ bất định
Đại từ bất định là những từ không chỉ cụ thể đến người hay vật nào đó mà chỉ nói một cách chung chung. Dưới đây là một số đại từ bất định phổ biến được hình thành từ 4 nhóm:
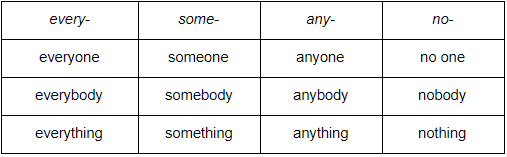
Tất cả các động từ chỉ hành động của đại từ bất định đều phải được chia số ít.
e.g. :
Something needs to be done about the increasing rate of crime.
According to the news, no one is directly responsible for the problems.
VI. Từ chỉ số lượng
Với danh từ đếm được số ít và danh từ không đếm được, động từ được chia số ít.
e.g. :
One-third of the article is taken up with statistical analysis.
Much of the book seems relevant to this study.
Half of what he writes is undocumented.
Fifty percent of the job is routine.
All the information is current
Với danh từ đếm được số nhiều, động từ cũng được chia số nhiều
e.g. :
One-third of the students have graduate degrees.
Many researchers depend on grants from industry.
Half of his articles are peer-reviewed.
Fifty percent of the computers have CD-ROM drives.
All the studies are current.
e.g. :
Half of my family lives in Canada. (Một nửa gia đình tôi sống ở Canada trong cùng một căn nhà nên được coi là một chủ thể thực hiện hành động.)
Half of my family live in Canada. (Một nửa gia đình tôi sống ở Canada nhưng mỗi người ở một nơi khác nhau trong Canada nên được coi là nhiều người thực hiện hành động.)
All of the class is/are here.
Ten percent of the population is/are bilingual.
Với các từ majority và minority:
The majority holds no strong views.
A small minority indicates it supports the proposal.
A majority of Canadians have voted for change.
A minority of the students are willing to pay more.
Ten dollars is a great deal of money to a child.
Ten kilometres is too far to walk.
Six weeks is not long enough.
The rich get richer.
The poor face many hardships.
Khi diễn tả một chủ thể thống nhất, động từ được chia số ít, sử dụng mạo từ ‘the’ trước ‘number of’:
The number of students registered in the class is 20.
Khi đóng vai trò định lượng từ bất định, động từ được chia số nhiều, sử dụng mạo từ ‘a’ trước ‘number of’:
A number of students were late.
Luyện tập
Bài 1: Chọn đáp án đúng
1. Apple as well as grape ………her favorite fruits.
a. has b. have c. is d. are
2. Neither Jane nor her sister ………exercise each morning.
a. do b. is doing c. does d. did
3. Drinking fruit juice…………..wonders for our health.
a. do b. is c. does d. have
4. John, along with twenty friends,……….planning a party.
a. are b. were c. is d. will
5. Reasons for this matter……………., but the most outstanding one is that people don’t like to travel a long way to pick up children afterschool.
a. has varied b. has been varied c. varies d. vary
6. Both Jane and Mary…………..going to Jimmy’s birthday party next Sunday.
a. has b. have c. are d. is
7. Physics………………..a difficult subject to some people.
a. was b. are c. is d. were
8. There……………100 people at the wedding yesterday.
a. was b. were c. are d. am
9. There……………an apple, 2 oranges and some bottles of milk on the table.
a. is b. are c. were d. being
10. There…………….several people at the convention hall now.
a. were b. are c. was d. is
Bài 2: Điền dạng đúng của động từ trong ngoặc
IELTS Writing Task 1
The diagrams below give information on transport and car use in Edmonton.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Sample answer:
The table (1. show)………………… the reason why people in Edmonton use their cars in the city and the pie chart (2. explain)………………… what type of transport is preferred most of the time.
Looking at the pie chart first, it is clear that the car (3. be)………………… the most popular means of transport in this city. 45% of the people (4. say)………………… that they prefer to commute by car. The second most popular form of transport (5. be)………………… the LRT, while busses and taxis (6. be)………………… the main means of transport for the rest of the people.
The table (7. give)………………… more detailed information about why people use their cars. Surprisingly, 55% of the people (8. need)………………… to commute to work by car. Cars (9. be)………………… also used a lot for taking children to school or business purposes. Only 15% of drivers (10. be)………………… doing their shopping and, similarly, 15% (11. need)………………… to travel by car for leisure.
Overall, people in Edmonton make good use of alternative methods of transport but there (12. be)………………… a heavy dependence on cars for work.